性能
Reduce Bundle Size
Code Splitting, Lazy Loading, load on the fly
Lazy 用以进行懒加载,Suspense 提供 loading state,用以优化延迟体验。
import React, { lazy, Suspense } from 'react';
const OtherComponent = lazy(() => import('./OtherComponent'));
function MyComponent() {
return (
<Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<OtherComponent />
</Suspense>
);
}
Avoid Re-rendering
触发 re-render 的情况:props 和 state 发生改变。所以我们能做的,围绕以下两点展开
- 减少 props 和 state 的改变,避免不必要的改变。
- 精确判断改变的内容,对无关改变不作响应。
Avoid Context
Context API 的更新可以穿透 React.memo 或者 shouldComponentUpdate 的比对,也就是说,一旦 Context 的 Value 变动,所有依赖该 Context 的组件会全部 forceUpdate。
Unique Key for Iteration
除非完全静态的 List,否则不可使用 index 作为 key。
完全静态 List,指的是不会进行插入、删除、排序,等等操作的 List。
Throttling and Debouncing Events
Throttling: delaying function execution.
use case: page scrolling, infinite scroll.
Debouncing: ignoring the event handler call until the calls have stopped for a certain amount of time.
use case: auto complete input
推荐 Lib: lodash, throttle-debounce.
Avoid Inline Function
we should bind function in constructor instead of use inline function. 二者区别如下:
- binding: prototype property of the class
- arrow function: object instance
此处有争议,有测试表明在高版本中二者性能无显著差异。
减少渲染次数
以下二种方法都是通过对 props 进行浅对比(shallow comparison) ,以及定制对比功能,来减少 rerender 次数。
- Function Components: React.memo(),
- 会记住对于确定的 props,最近一次渲染的结果,直接复用;、
- 对于 props 的改变,进行 shallow comparison。
- 可以传入第二个参数,定制 comparator (previousProps, nextProps) ⇒ true or false
- Class Components: PureComponent
- 概念类似纯函数,相同的 props 和 state,相同的 output。
- extends PureComponent,shouldComponentUpdate 中进行了 shallow comparison
- 定制 props/state 对比: shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState)
// only rerenders if props change
const MyComponent = React.memo(function MyComponent(props) {}, areEqual);
function areEqual(prevProps, nextProps) {
/*
return true if passing nextProps to render would return
the same result as passing prevProps to render,
otherwise return false
*/
}
useMemo, useCallback ,避免属性改变以及昂贵计算
// useCallback(fn, deps) is equivalent to useMemo(() => fn, deps).
const memoizedCallback = useCallback(() => {
doSomething(a, b);
}, [a, b]);
const memoizedValue = useMemo(() => computeExpensiveValue(a, b), [a, b]);
useCallback(fn, deps);
// is equivalent to
useMemo(() => fn, deps);
useRef 持久化保存变量
const debouncedFetchOptions = useRef(_.debounce(fetchOptions, 500));
useEffect(() => {
debouncedFetchOptions.current(id, searchContent);
}, [id, searchContent]);
降低渲染的复杂度
大概有三个思路
- 减少渲染的节点数
- 减少计算复杂性,减少计算量
- 减少计算的复杂度
Avoid Side Effects in Render
保证 render: pure function. setState, query DOM 之类的不要做
React Fragments
减少节点数
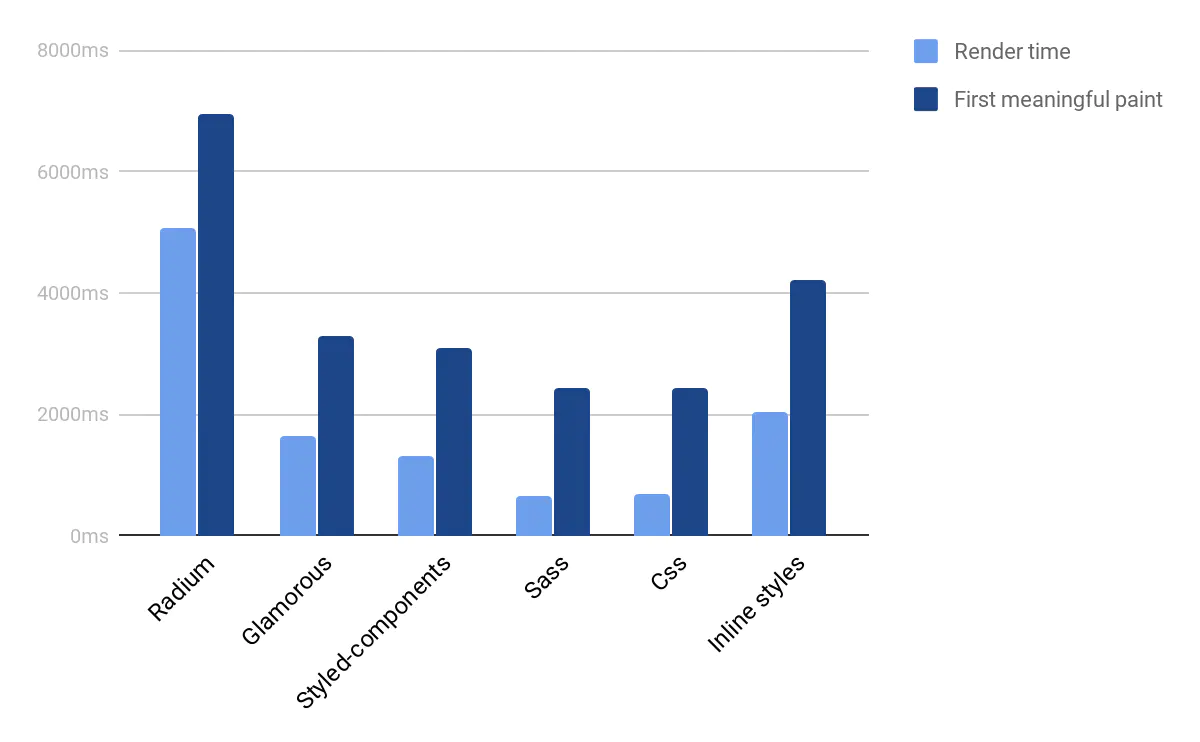
Avoid Inline Style
减少不必要的嵌套 styled-components,过多的嵌套 DOM 节点很消耗计算性能
渲染性能:CSS > 大部分CSS-in-js > inline style
虚拟列表
只渲染当前window 可见元素,推荐 react-window
条件语句
固定的部分,不要写进条件语句
Error Boundaries
getDerivedStateFromError
componentDidCatch
Immutable Data Structures for Components
有利于 React 快速精确地对 props 改变进行判断。缺点是主流 Lib 需要一定的心智负担。
Tools
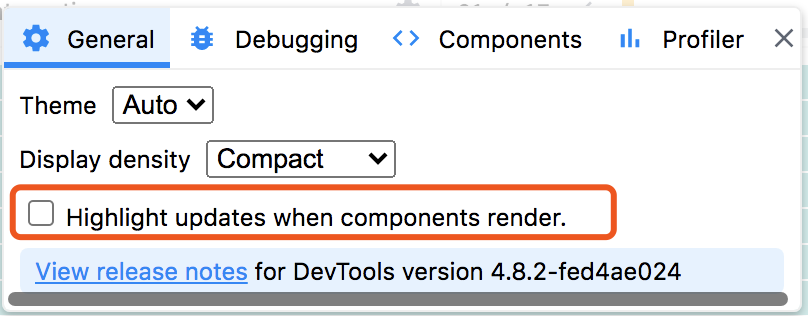
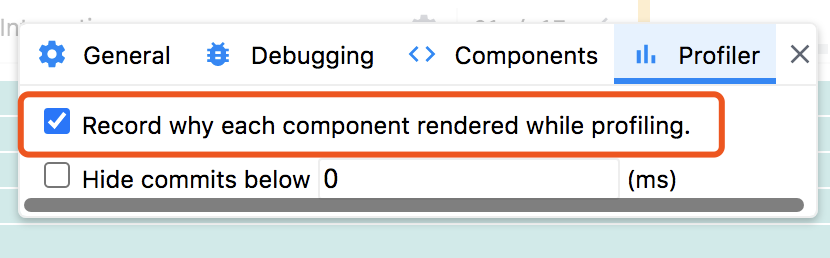
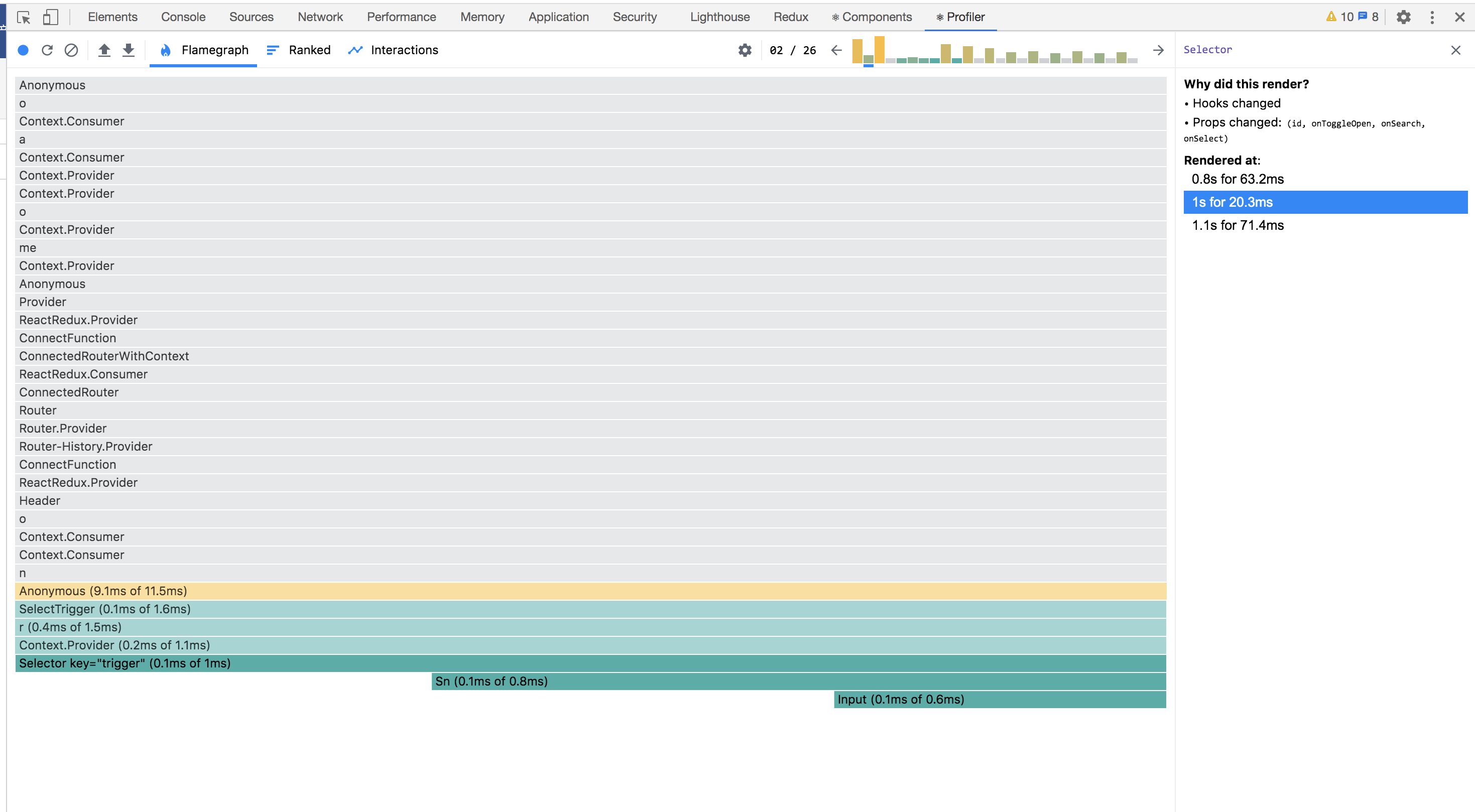
React Devtool Profiler
- Highlight updates when components render.
- Record why each component rendered while profiling.
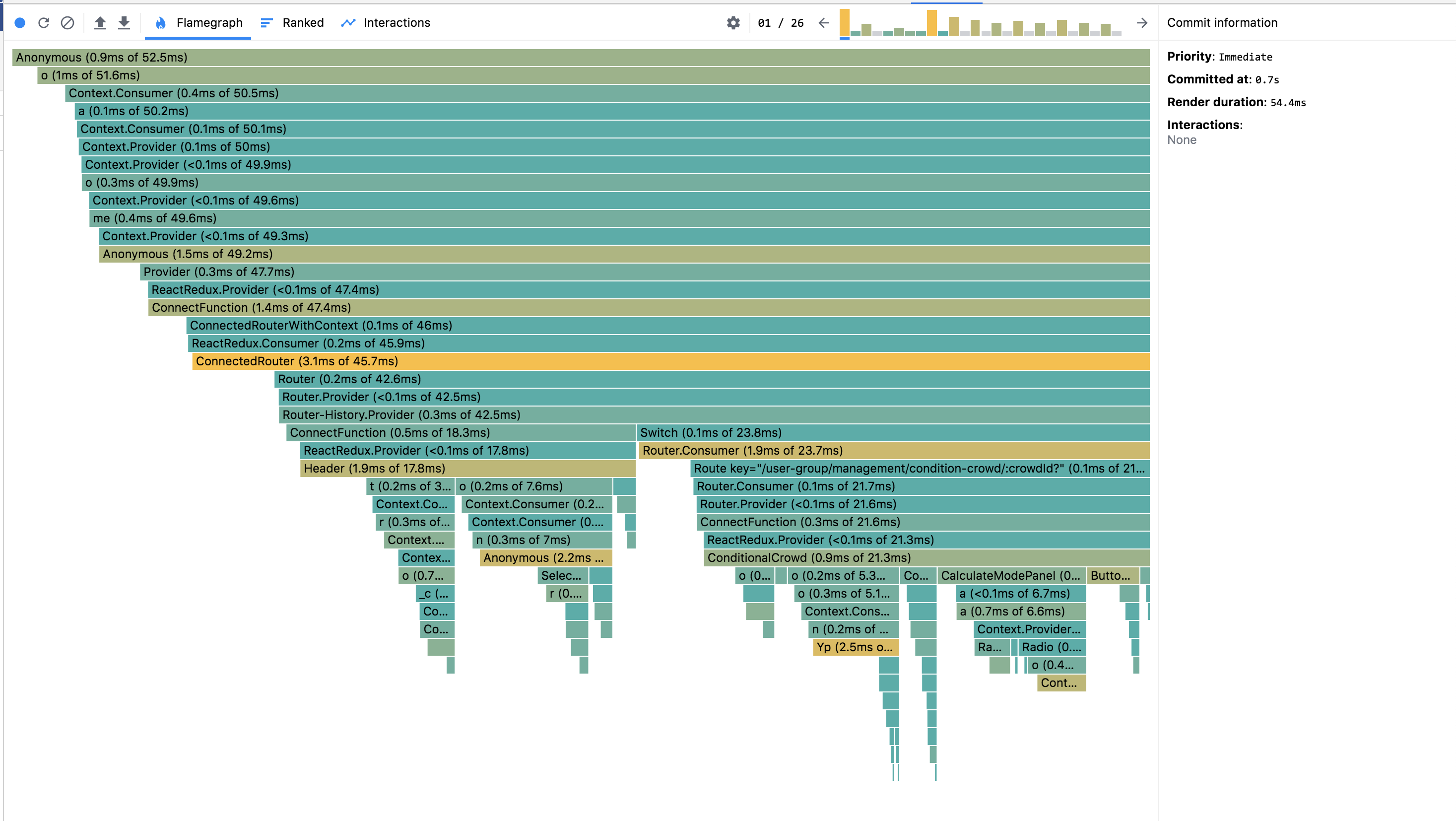
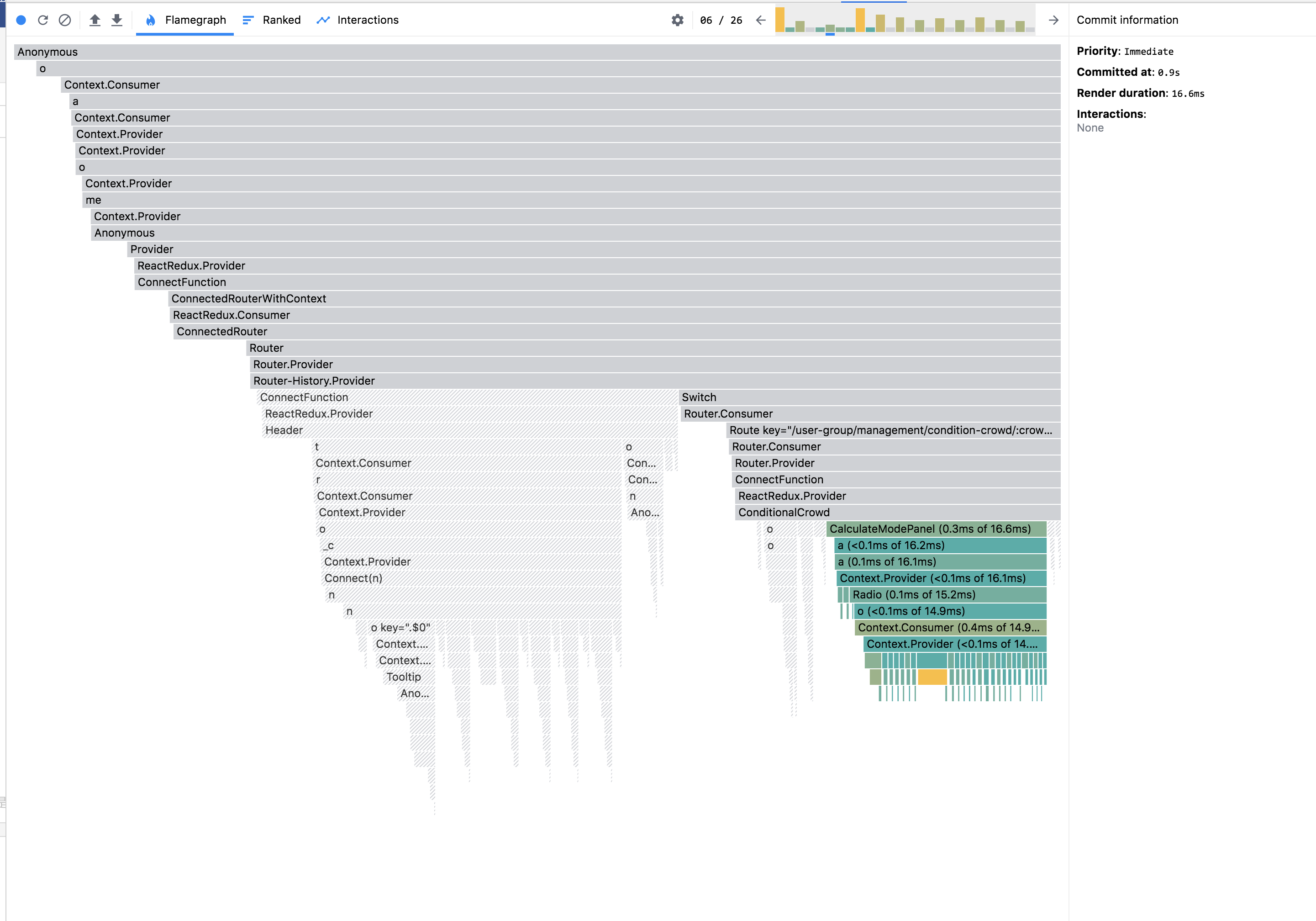
打开记录后,可以针对 Commit List 对组件的渲染情况有一个深入的了解。
灰色:未重新渲染
消耗时间:黑色>黄色>绿色