Dijkstra
大名鼎鼎的最短路径算法,不再赘述
数据结构
// 输入,每个节点的next节点,距离;以及是否遍历过改节点
const graph = {
A: {
neighbours: {
B: 22,
...
},
done: false;
},
B: {...},
...
}
// 每个节点的最小cost
const = {
A: 0,
B: 22,
...
}
// 最小cost对应的前一节点
parent = {
A: 'B'
}
算法步骤
- 找出距离最短的节点
- 遍历其 neighbours
- 如果计算出 neighbour 的 cost 小于其当前 cost,更新 neighbour 的 cost
- 对该节点标记完成
- 重复上述步骤。
示例
如下图所示,寻找从 起点 A 到 终点 F 的最短路径。
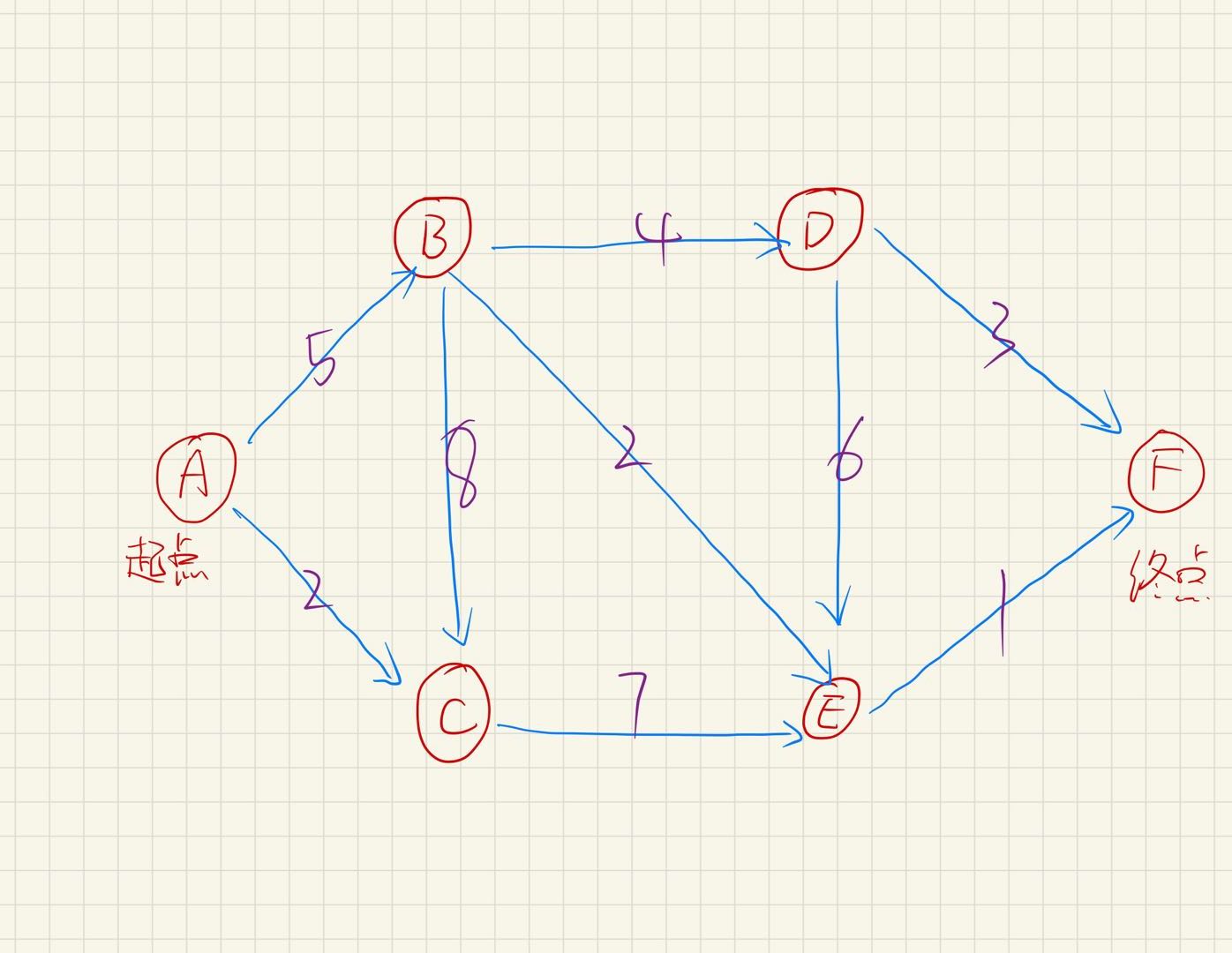
// graph, 用以描述问题
const graph = {
A: { neighbours: { B: 5, C: 2 }, done: false },
B: { neighbours: { D: 4, E: 2 }, done: false },
C: { neighbours: { B: 8, E: 7 }, done: false },
D: { neighbours: { E: 6, F: 3 }, done: false },
E: { neighbours: { F: 1 }, done: false },
F: { neighbours: {}, done: false }
};
// 获取未处理的,最近的点
const getNearestNode = (costs, graph) => {
const sortedKeys = Object.keys(costs)
.filter(key => !graph[key].done)
.sort((a, b) => costs[a] - costs[b]);
return sortedKeys[0];
};
function dijkstra(graph) {
// 先记录起始点,为0
const costs = {
A: 0
};
const parents = {};
let key;
while ((key = getNearestNode(costs, graph))) {
const nbs = graph[key].neighbours;
for (const nb of Object.keys(nbs)) {
const cost = costs[key];
if (!costs[nb] || costs[nb] > cost + nbs[nb]) {
costs[nb] = cost + nbs[nb];
parents[nb] = key;
}
}
graph[key].done = true;
}
console.log(costs);
console.log(parents);
}
dijkstra(graph);
// 结果如下
// costs
{ A: 0, B: 5, C: 2, E: 7, D: 9, F: 8 }
// parents
{ B: 'A', C: 'A', E: 'B', D: 'B', F: 'E' }
应用
Leetcode 743. Network Delay Time
代码如下
/**
* @param {number[][]} times
* @param {number} N
* @param {number} K
* @return {number}
*/
const generateGraph = times => {
const graph = {};
for (const [t0, t1, t2] of times) {
if (!graph[t0]) {
graph[t0] = { neighbours: {} };
}
if (!graph[t1]) {
graph[t1] = { neighbours: {} };
}
graph[t0].neighbours[t1] = t2;
}
return graph;
};
const getNearestNode = (costs, graph) => {
const sortedKeys = Object.keys(costs)
.filter(key => !graph[key].done)
.sort((a, b) => costs[a] - costs[b]);
return sortedKeys[0];
};
var networkDelayTime = function (times, N, K) {
const graph = generateGraph(times);
const costs = { [K]: 0 };
const parents = {};
let key;
while ((key = getNearestNode(costs, graph))) {
const nbs = graph[key].neighbours;
for (const nb of Object.keys(nbs)) {
const cost = costs[key];
if (costs[nb] === undefined || costs[nb] > cost + nbs[nb]) {
costs[nb] = cost + nbs[nb];
parents[nb] = key;
}
}
graph[key].done = true;
}
if (Object.keys(costs).length !== N) {
return -1;
}
return Math.max(...Object.values(costs));
};
console.log(
networkDelayTime(
[
[2, 1, 1],
[2, 3, 1],
[3, 4, 1],
],
4,
2,
),
);
console.log(
networkDelayTime(
[
[1, 2, 1],
[2, 1, 3],
],
2,
2,
),
);